
INSERM Research Fellow,
fatima.clerc@inserm.fr
The incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has greatly increased over the past 30 years and is a major public health issue. Local inflammation is an important risk factor for the development of HCC. Thus, clarification of the mechanisms underlying the role of inflammation in the initiation and progression of HCC is necessary to identify new therapeutic targets.
Among immune cells, macrophages represent the major inflammatory component of tumor stroma and their density within tumors is closely linked to a poor prognosis. Macrophages play a role in all stages of tumorigenesis: tumoral transformation, cellular proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Additionally, macrophages exhibit great plasticity and can be pro- or anti-tumoral, depending on their polarization state, making them valuable therapeutic targets.
Clarification of the mechanisms underlying the role of inflammation in the initiation and progression of HCC is necessary to identify new therapeutic targets. Our general objective is to improve our understanding of the cellular and molecular mechanisms of inflammation-mediated hepatocarcinogenesis, interactions between tumors and immune cells, and the contribution of macrophages to these processes, with the ultimate goal of identifying new targets for prevention and/or treatment of HCC.
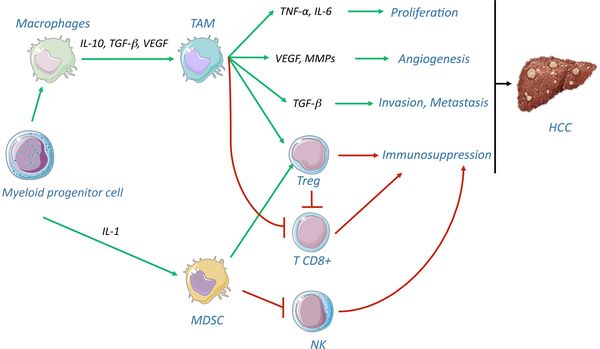
Role of myeloid cells in HCC
The tumoral microenvironment induces the differentiation of myeloid cells to immunoregulatory cells, such as tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC). TAM and MDSC play a pro-tumoral role by inducing proliferation, angiogenesis, invasion, and immunosuppression, particularly by stimulating the generation of regulatory T lymphocytes and inhibiting CD8-positive T-cell effector functions and natural killer (NK) cells.
TAM: tumor-associated macrophages, MDSC: myeloid-derived suppressor cells, Treg: regulatory T cells, CD8+: cytotoxic T cells, NK: Natural Killer cells.
The Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Protects Against Alcoholic Liver Disease Via a Macrophage Autophagy-Dependent Pathway
Sci Rep. 2016
Macrophage autophagy protects against liver fibrosis in mice
Autophagy 2015
Autophagy: a multifaceted partner in liver fibrosis
Biomed Res Int. 2014
Cannabinoid CB2 receptors protect against alcoholic liver disease by regulating Kupffer cell polarization in mice
Hepatology 2011
Beneficial paracrine effects of cannabinoid receptor 2 on liver injury and regeneration
Hepatology 2010